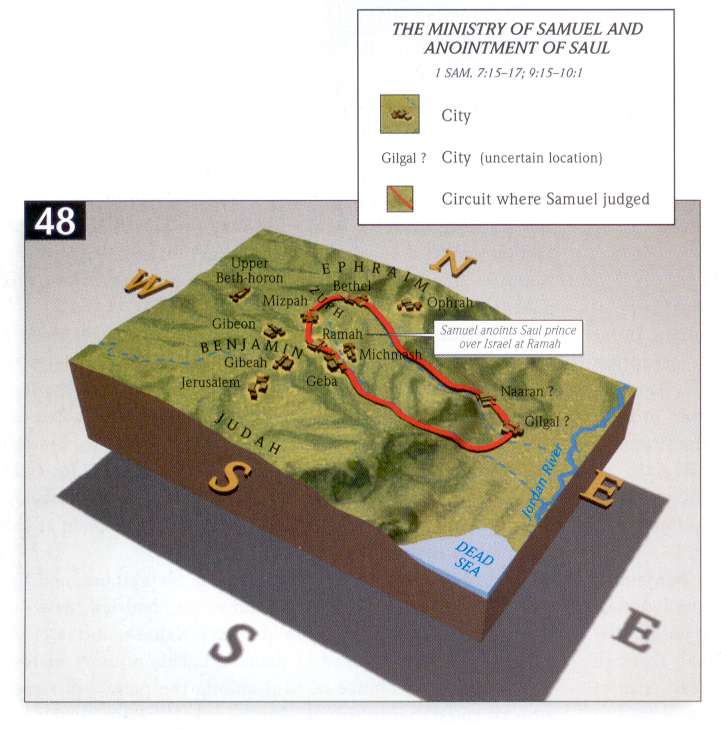
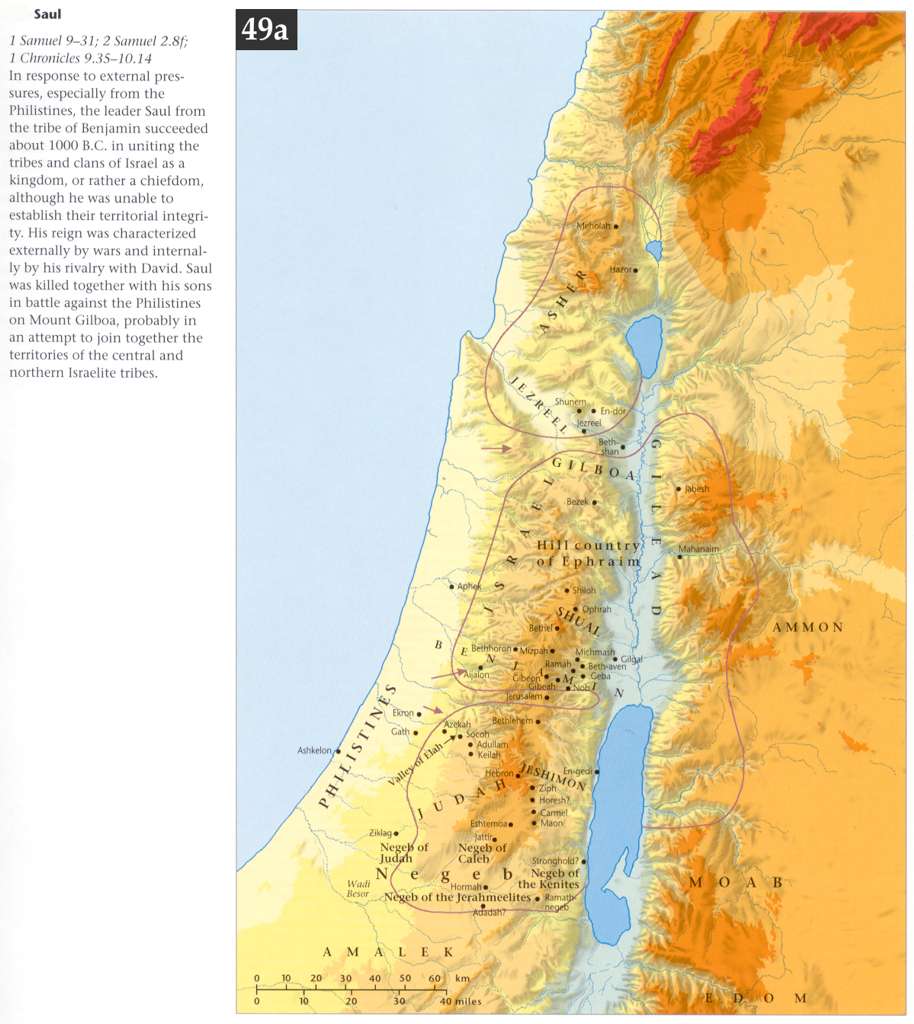
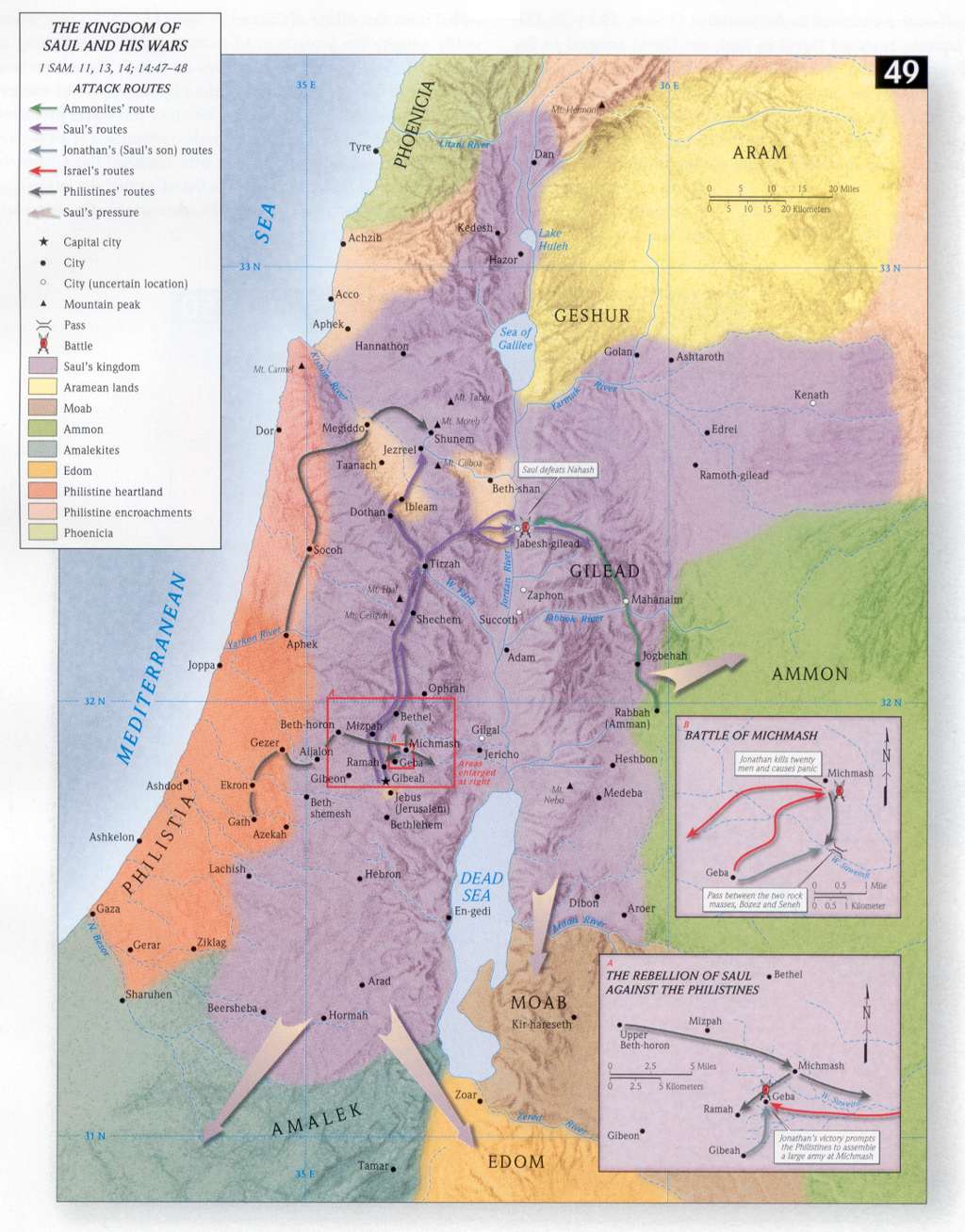
1 Samuel 14:47
Bible Commentary
So Saul took the kingdom - The Targum appears to give the meaning of this expression: "Saul prospered in his government over Israel." And the proofs of his prosperity are immediately subjoined.
Fought against all his enemies - Of the wars which are mentioned here we have no particulars; they must have endured a long time, and have been, at least in general, successful.
Notes on the Whole Bible
Compare 2 Samuel 8:15. The preceding narrative shows that before this time Saul had been king in name only, since his country was occupied by the Philistines, and he could only muster 600 men, and those but half armed and pent up in a narrow stronghold. Now, however, on the expulsion of the Philistines from his country, and the return of the Israelites from their vassalage and from their hiding places 1 Samuel 14:21-22, Saul became king in deed as well as in name, and acted the part of a king through the rest of his reign in defending his people against their enemies round about. A comprehensive list of these enemies, including the Ammonite war which had already been described 1 Samuel 11:1-15, and the Amalekite war which follows in 1 Samuel 14:47-48. There is not the slightest indication from the words whether this “taking the kingdom” occurred soon or really years after Saul‘s anointing at Gilgal. Hence, some would place the clause 1 Samuel 14:47-52 immediately after 1 Samuel 11:1-15, or 1 Samuel 31:1-13, preceded by the formulary, 1 Samuel 13:1, would then follow according to the common method of Hebrew historical narrative.
Zobah - This was one of the petty Ara-roman kingdoms flourishing at this time (Psalm 60:1-12 title). It seems to have been situated between Damascus and the Euphrates.
Concise Bible Commentary
Patriarchs and Prophets, 628-9
The forbearance that God has exercised toward the wicked, emboldens men in transgression; but their punishment will be none the less certain and terrible for being long delayed. “The Lord shall rise up as in Mount Perazim, He shall be wroth as in the valley of Gibeon, that He may do His work, His strange work; and bring to pass His act, His strange act.” Isaiah 28:21. To our merciful God the act of punishment is a strange act. “As I live, saith the Lord God, I have no pleasure in the death of the wicked; but that the wicked turn from his way and live.” Ezekiel 33:11. The Lord is “merciful and gracious, long-suffering, and abundant in goodness and truth, ... forgiving iniquity and transgression and sin.” Yet He will “by no means clear the guilty.” Exodus 34:6, 7. While He does not delight in vengeance, He will execute judgment upon the transgressors of His law. He is forced to do this, to preserve the inhabitants of the earth from utter depravity and ruin. In order to save some He must cut off those who have become hardened in sin. “The Lord is slow to anger, and great in power, and will not at all acquit the wicked.” Nahum 1:3. By terrible things in righteousness He will vindicate the authority of His downtrodden law. And the very fact of His reluctance to execute justice testifies to the enormity of the sins that call forth His judgments and to the severity of the retribution awaiting the transgressor. PP 628.1
But while inflicting judgment, God remembered mercy. The Amalekites were to be destroyed, but the Kenites, who dwelt among them, were spared. This people, though not wholly free from idolatry, were worshipers of God and were friendly to Israel. Of this tribe was the brother-in-law of Moses, Hobab, who had accompanied the Israelites in their travels through the wilderness, and by his knowledge of the country had rendered them valuable assistance. PP 628.2
Since the defeat of the Philistines at Michmash, Saul had made war against Moab, Ammon, and Edom, and against the Amalekites and the Philistines; and wherever he turned his arms, he gained fresh victories. On receiving the commission against the Amalekites, he at once proclaimed war. To his own authority was added that of the prophet, and at the call to battle the men of Israel flocked to his standard. The expedition was not to be entered upon for the purpose of self-aggrandizement; the Israelites were not to receive either the honor of the conquest or the spoils of their enemies. They were to engage in the war solely as an act of obedience to God, for the purpose of executing His judgment upon the Amalekites. God intended that all nations should behold the doom of that people that had defied His sovereignty, and should mark that they were destroyed by the very people whom they had despised. PP 628.3
Read in context »